“Threat actors never sleep…. neither can your security.” These reverberating lines by Jonathan Jackson (Director, Sales Engineering, APJ) reflect the significance of a multi-layered security system for organizations, enterprises, and startups, predominantly to safeguard resources (assets and financials) and ensure optimal growth. Fortify your enterprise with advanced endpoint security. Novasecuris ensures robust protection, safeguarding endpoints from evolving cyber threats
Endpoint security systems protect data and workflows correlated with electronic devices that link to the entire network. It works with a centralized management console installed on a server or network, enabling admins to control security. The software is positioned at each endpoint to render systematic updates when necessary.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Enterprise Endpoint Security?
Companies or businesses linking to multiple endpoints (physical devices that exchange information or connect to a computer system), become key targets for cyber criminals. Upon infiltration, the entire system grinds to a halt. Enterprises, therefore, opt for an infallible modern-day security system with advanced features, such as 24/7 monitoring and assessment: Endpoint security is viewed as the first line of defense by cyber experts.
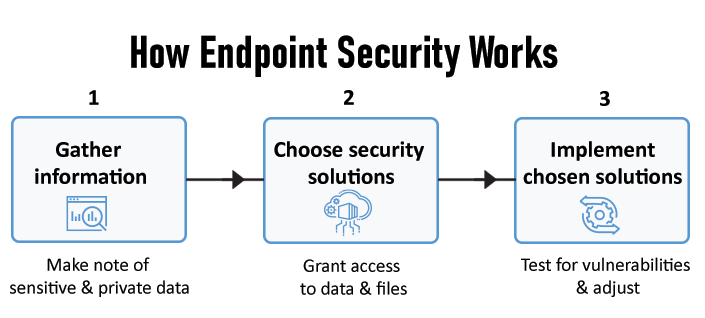
Types of Enterprise Endpoint Security
Enterprise endpoint security measures depend on the cyber threat’s severity. There are three main types of EES:
1. Endpoint Protection Platform
This process helps to prevent malware and other similar threats. It acts as a reactive antivirus program.
2. Endpoint Detection and Response
EDR systems muster and analyze threat-based data from workstations and other endpoints, with the aim of targeting threats and flagging investigations.
3. Extended Detection and Response
XDR, or Extended Detection and Response offers threat detection and elimination by assimilating information across networks, endpoints, and cloud applications.
Complications in Enterprise Endpoint Security
The IT landscape (networks, laptops, smartphones, etc.) is under constant threat from cyberattacks, much to the issue of unresolved vulnerabilities in organizations and corporations. Although endpoint security measures play their role effectively, there are lapses that prevail.
1. Lack of Visibility
Compared to MDR and XDR potentialities, EDR (endpoint detection and response) extracts and examines limited information regarding cyber threats. This creates a gaping hole for unwanted intrusions to act spontaneously. In such situations, enterprises should opt for high-end solutions like MDR or EDR with additional reinforcements (behavioral analysis, network traffic analysis tools, etc.)
A potent disadvantage for IT companies is ‘invisible devices’ or ‘remote endpoints‘ (physical instruments that are beyond the radar of the company). Several problems may arise, such as improper connections with work laptops on home networks, use of VPN tools, and irregular link with the domain.
2. Unattended Alerts
Every detection and response service flags information for scrutiny and assessment. Security teams, thereafter, identify and address threats, ensuring a smooth working environment. This process works proportionally: The higher the quantity of endpoints, the more the volume of logs for experts to assess. However, at times, some attacks may go undetected because of excess overload. Such mistakes are liable to security breaches that may take several hours or days to discover and remediate from the system.
3. Mobile Devices/BYOD
Tracking and analyzing cell phones is one of the most essential features of endpoint security. However, the process is becoming difficult to comprehend, with the advent of BYOD policies. The best solution is to assess and evaluate the type of mobile devices connected to the network. It helps to determine if the solution can meet the demands and scale to accommodate increase in cell phones as time progresses.
If a mobile device goes missing, the security team should be able to wipe, lock, or factory reset it to restrict information from being accessed or embezzled. Or, if an endpoint is infected with a malicious code, they can reimage the device completely.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Proper compliance is mandatory for cybersecurity companies. It enables organizations to analyze risks, protect data, and follow a plan in case of a breach. However, with the increase in endpoints in recent years, authorities are constantly changing laws to manage the intensity of security breaches. Each law entails different goals and mandates. And, most of them require local admin privileges to inhibit disagreements and security risks.
Why is Compliance Important?
- Boosts Trust
- Reduces Loss
- Develops Security Posture
- Reinforces Control
5. Secured Ports
Besides computer systems, tablets, mobile phones, and printers, USB ports are also an important endpoint. To ensure safety for a corporate network, the ports are locked and kept under strict control. Unsecured USB ports can be used to embezzle information or introduce malicious software in the network.
Cybersecurity firms implement the least-privilege strategy to counter different threats: This approach helps to limit access to USB ports, restrict unwanted intrusion in form of malware and data theft, and maintain zero trust standards.
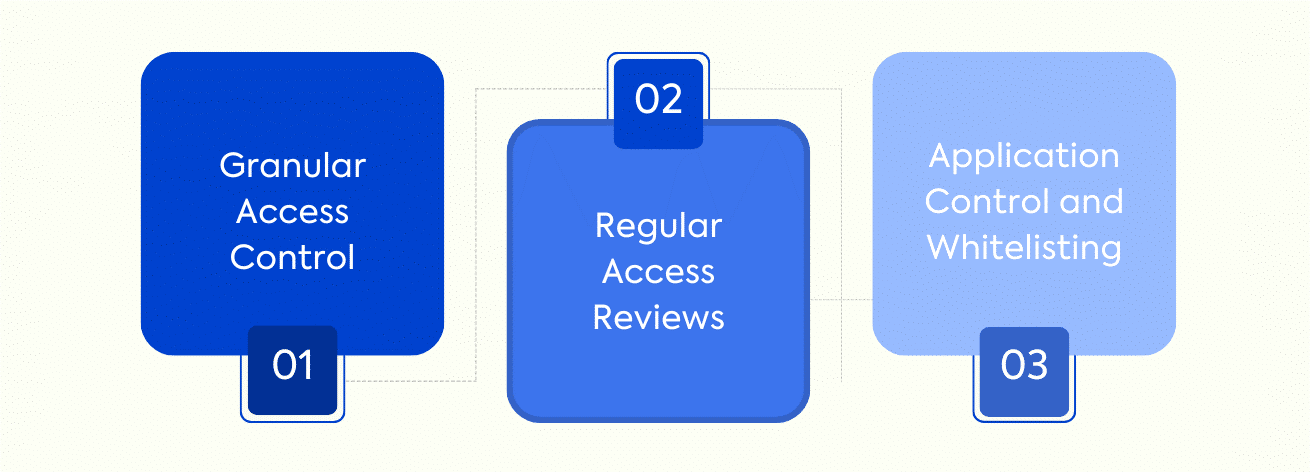
Effective Measures to Reinforce Enterprise Endpoint Security
“With advanced threats, come advanced solutions”. Implementation of endpoint strategies are necessary for enterprises and firms to function smoothly. Following are some viable solutions:
- Targeted UEM Strategy
- Requirement of Digital Certificate Management
- Patch Management System
- Shadow IT
Enterprise endpoint security systems have been in the limelight since the technology boost and the introduction of new devices. Companies have opted for various services, ranging from EPP (Endpoint Protection Platform), EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response), MDR (Managed Detection and Response), etc. Opt for your preferred security system and relish the experience.
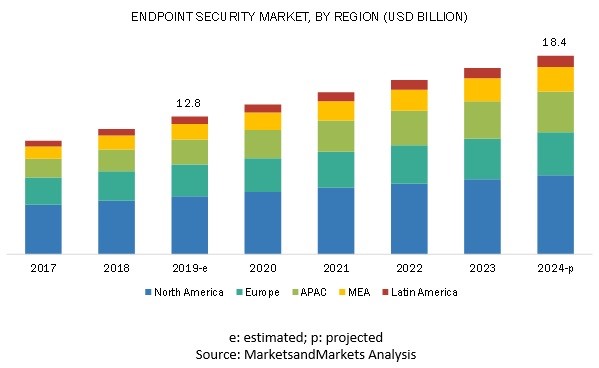
Statistics & Projections
According to Market and Markets Analysis, the estimated endpoint security market (by region) will reach 18.4 billion by 2024.
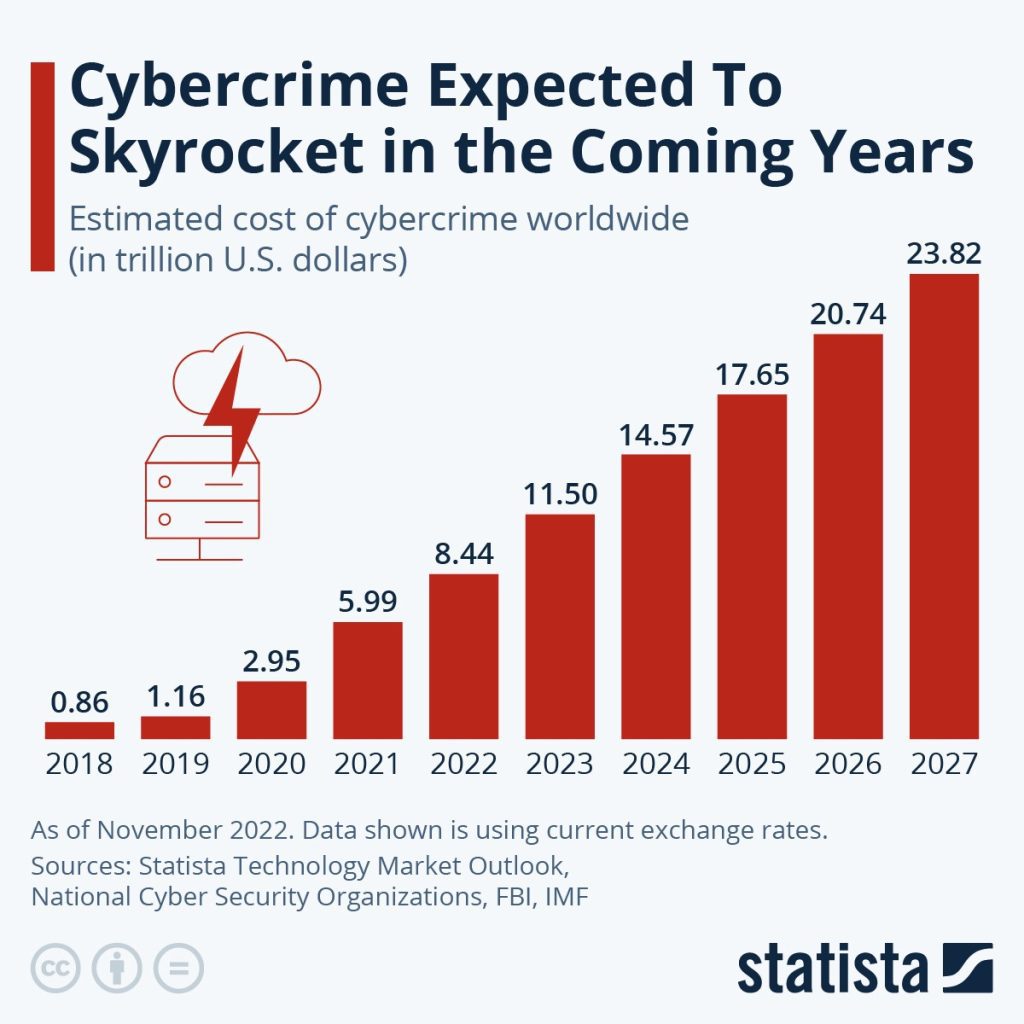
According to Statistica, the quantity of cybercrime is expected to augment in the years ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1. What are the common kinds of endpoint threats?
Ans. The common kinds of endpoint security issues are:
- Malware
- DDoS (Denial of Service) Attacks
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
- SQL Injection Attacks
- Social Engineering Attacks
Q.2. What is the role of antivirus in endpoint security?
Ans. The antivirus system offers a reliable defensive mechanism against phishing, malware, and other threats. It is also used to verify spams in email and malicious website links.
Q.3. What is patch management feature in endpoint security?
Ans. Patch management helps to maintain networks and equipment updated with modern-day security fixes. Security teams can fix patches across the entire network in quick time.


